1. 线性布局(LinearLayout)
线性布局的形式可以分为两种,第一种横向线性布局 第二种纵向线性布局,总而言之都是以线性的形式 一个个排列出来的,纯线性布局的缺点是很不方便修改控件的显示位置,所以开发中经常会 以 线性布局与相对布局嵌套的形式设置布局。

如图所示 使用了线性布局的水平方向与垂直方向,从图中可以清晰的看出来所有控件都是按照线性的排列方式显示出来的,这就是线性布局的特点。设置线性布局为水平方向
android:orientation=”horizontal”
设置线性布局为垂直方向
android:orientation=”vertical”
设置正比例分配控件范围
android:layout_weight=”1″
设置控件显示位置,这里为水平居中
android:gravity=”center_horizontal”在xml中我使用了LinearLayout 嵌套的方式 配置了2个线性布局 一个水平显示 一个垂直显示。
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- android:orientation="vertical"
- >
- <LinearLayout
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- android:orientation="horizontal"
- android:gravity="center_horizontal"
- android:layout_weight="2"
- >
- <ImageView
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:src="@drawable/jay"
- />
- <TextView
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="雨松MOMO"
- android:background="#FF0000"
- android:textColor="#000000"
- android:textSize="18dip"
- />
- <EditText
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="水平方向"
- />
- </LinearLayout>
- <LinearLayout
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- android:orientation="vertical"
- android:layout_weight="1"
- >
- <TextView
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="雨松MOMO"
- android:background="#FF0000"
- android:textColor="#000000"
- android:textSize="18dip"
- />
- <EditText
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="垂直方向"
- />
- <Button
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="雨松MOMO"
- />
- <ImageView
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:src="@drawable/image"
- />
- </LinearLayout>
- </LinearLayout>
2. 相对布局(RelativeLayout)
相对布局是android布局中最为强大的,首先它可以设置的属性是最多了,其次它可以做的事情也是最多的。android手机屏幕的分辨率五花八门所以为了考虑屏幕自适应的情况所以在开发中建议大家都去使用相对布局 它的坐标取值范围都是相对的所以使用它来做自适应屏幕是正确的。

设置距父元素右对齐
android:layout_alignParentRight=”true”
设置该控件在id为re_edit_0控件的下方
android:layout_below=”@id/re_edit_0″
设置该控件在id为re_image_0控件的左边
android:layout_toLeftOf=”@id/re_iamge_0″
设置当前控件与id为name控件的上方对齐
android:layout_alignTop=”@id/name”
设置偏移的像素值
android:layout_marginRight=”30dip”
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- >
- <EditText
- android:id="@+id/re_edit_0"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="雨松MOMO"
- android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
- />
- <ImageView
- android:id="@+id/re_iamge_0"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:src="@drawable/jay"
- android:layout_below="@id/re_edit_0"
- android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
- />
- <TextView
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:background="#FF0000"
- android:text="努力学习"
- android:textColor="#000000"
- android:textSize="18dip"
- android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/re_iamge_0"
- />
- <EditText
- android:id="@+id/re_edit_1"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="雨松MOMO"
- android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
- />
- <ImageView
- android:id="@+id/re_iamge_1"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:src="@drawable/image"
- android:layout_above="@id/re_edit_1"
- />
- <TextView
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:background="#FF0000"
- android:text="努力工作"
- android:textColor="#000000"
- android:textSize="18dip"
- android:layout_toRightOf="@id/re_iamge_1"
- android:layout_above="@id/re_edit_1"
- />
- </RelativeLayout>
3. 帧布局(FrameLayout)
原理是在控件中绘制任何一个控件都可以被后绘制的控件覆盖,最后绘制的控件会盖住之前的控件。如图所示界面中先绘制的ImageView 然后在绘制的TextView和EditView 所以后者就覆盖在了前者上面。
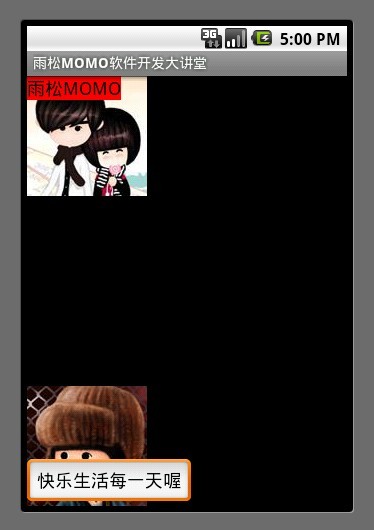
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <FrameLayout
- xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent">
- <ImageView
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:src="@drawable/g"
- />
- <TextView
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="雨松MOMO"
- android:background="#FF0000"
- android:textColor="#000000"
- android:textSize="18dip"
- />
- <ImageView
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:src="@drawable/image"
- android:layout_gravity="bottom"
- />
- <EditText
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="快乐生活每一天喔"
- android:layout_gravity="bottom"
- />
- </FrameLayout>
4. 绝对布局(AbsoluteLayout)
使用绝对布局可以设置任意控件的 在屏幕中 X Y 坐标点,和帧布局一样后绘制的控件会覆盖住之前绘制的控件,笔者不建议大家使用绝对布局还是那句话因为android的手机分辨率五花八门所以使用绝对布局的话在其它分辨率的手机上就无法正常的显示了。

设置控件的坐标
- android:layout_x="50dip"
- android:layout_y="30dip"
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <AbsoluteLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent">
- <ImageView
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:src="@drawable/f"
- android:layout_x="100dip"
- android:layout_y="50dip"
- />
- <TextView
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="当前坐标点 x = 100dip y = 50 dip"
- android:background="#FFFFFF"
- android:textColor="#FF0000"
- android:textSize="18dip"
- android:layout_x="50dip"
- android:layout_y="30dip"
- />
- <ImageView
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:src="@drawable/h"
- android:layout_x="50dip"
- android:layout_y="300dip"
- />
- <TextView
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="当前坐标点 x = 50dip y = 300 dip"
- android:background="#FFFFFF"
- android:textColor="#FF0000"
- android:textSize="18dip"
- android:layout_x="30dip"
- android:layout_y="280dip"
- />
- </AbsoluteLayout>
5. 表格布局(TableLayout)
在表格布局中可以设置TableRow 可以设置 表格中每一行显示的内容 以及位置 ,可以设置显示的缩进,对齐的方式。
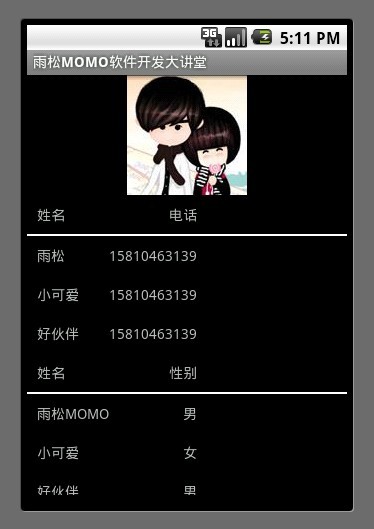
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- >
- <ImageView
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:src="@drawable/g"
- android:layout_gravity="center"
- />
- <TableRow
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- android:padding="10dip">
- <TextView
- android:text="姓名"
- android:gravity="left"
- />
- <TextView
- android:text="电话"
- android:gravity="right"/>
- </TableRow>
- <View
- android:layout_height="2dip"
- android:background="#FFFFFF" />
- <TableRow
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- android:padding="10dip">
- <TextView
- android:text="雨松"
- android:gravity="left"
- />
- <TextView
- android:text="15810463139"
- android:gravity="right"/>
- </TableRow>
- <TableRow
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- android:padding="10dip">
- <TextView
- android:text="小可爱"
- android:gravity="left"
- />
- <TextView
- android:text="15810463139"
- android:gravity="right"/>
- </TableRow>
- <TableRow
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- android:padding="10dip">
- <TextView
- android:text="好伙伴"
- android:gravity="left"
- />
- <TextView
- android:text="15810463139"
- android:gravity="right"/>
- </TableRow>
- <TableRow
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- android:padding="10dip"
- >
- <TextView
- android:text="姓名"
- android:gravity="left"
- />
- <TextView
- android:text="性别"
- android:gravity="right"/>
- </TableRow>
- <View
- android:layout_height="2dip"
- android:background="#FFFFFF" />
- <TableRow
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- android:padding="10dip"
- >
- <TextView
- android:text="雨松MOMO"
- android:gravity="left"
- />
- <TextView
- android:text="男"
- android:gravity="right"/>
- </TableRow>
- <TableRow
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- android:padding="10dip">
- <TextView
- android:text="小可爱"
- android:gravity="left"
- />
- <TextView
- android:text="女"
- android:gravity="right"/>
- </TableRow>
- <TableRow
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- android:padding="10dip">
- <TextView
- android:text="好伙伴"
- android:gravity="left"
- />
- <TextView
- android:text="男"
- android:gravity="right"/>
- </TableRow>
- </TableLayout>
Android五大布局的基本使用方法已经介绍完,最后笔者在这里强调一下在开发与学习中建议大家使用相对布局,首先它的方法属性是最强大的其次它基本可以实现其它4大布局的效果,当然这里说的不是全部 有时候还是须要使用其他布局, 所以笔者建议大家开发中以实际情况定夺,以上五种布局可以使用布局嵌套的方式可以做出更好看的更美观的布局。
源码下载地址:http://vdisk.weibo.com/s/aa2C2


发表评论:
◎欢迎参与讨论,请在这里发表您的看法、交流您的观点。